Introduction:
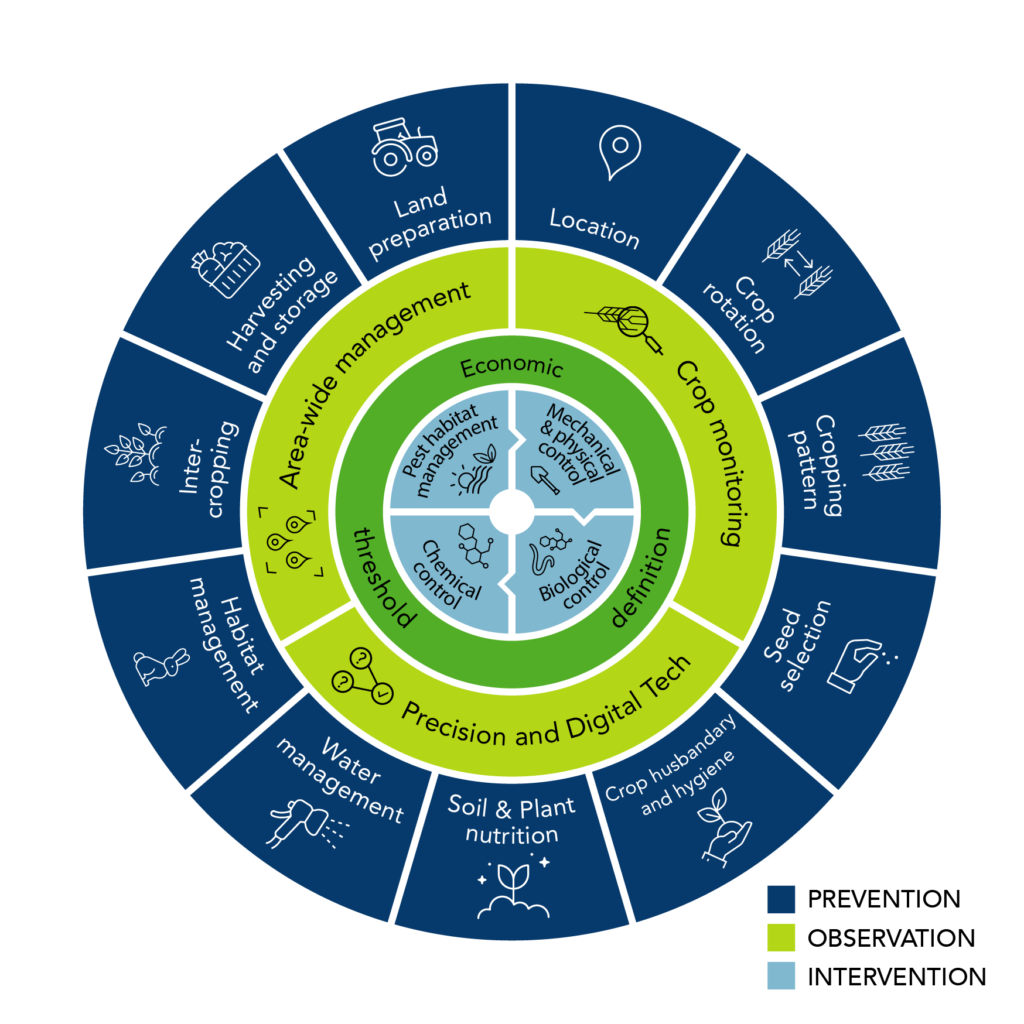
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) has emerged as a holistic and sustainable approach to pest control. Unlike traditional methods that rely heavily on chemical solutions, IPM combines various techniques to effectively manage pests while minimizing environmental impact.
Understanding Integrated Pest Management:
At the core of IPM is the integration of diverse strategies to control and prevent pest infestations. This comprehensive approach involves biological controls, cultural practices, and the strategic use of pesticides when necessary. By considering the ecosystem as a whole, IPM seeks to maintain a balance that disrupts pest activity without causing harm to non-target species.
Biological Controls in IPM:
One key pillar of IPM is the implementation of biological controls. This involves introducing natural predators or parasites to keep pest populations in check. By encouraging the presence of beneficial organisms, such as ladybugs or predatory insects, IPM promotes a sustainable and self-regulating ecosystem that minimizes the need for chemical interventions.
Cultural Practices for Pest Management:
IPM emphasizes the importance of cultural practices that create an environment less conducive to pest infestations. This includes proper waste management, crop rotation, and maintaining optimal plant health. These practices disrupt the life cycle of pests and reduce their ability to thrive, providing a long-term and environmentally friendly solution.
Monitoring and Early Detection:
A crucial aspect of IPM is regular monitoring to detect pest issues at an early stage. By identifying problems before they escalate, targeted interventions can be implemented, reducing the reliance on broad-spectrum pesticides. This proactive approach enhances the overall effectiveness of pest management while minimizing the ecological footprint.
Strategic Pesticide Use in IPM:
While minimizing pesticide use is a key goal of IPM, there are instances where strategic application is necessary. However, unlike traditional pest control methods that often involve routine spraying, IPM focuses on targeted and judicious use of pesticides. This approach minimizes the impact on non-target species and prevents the development of pesticide-resistant pests.
Benefits of Integrated Pest Management:
The benefits of adopting IPM are multifaceted. Not only does it reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides, but it also promotes environmental sustainability, protects beneficial organisms, and preserves biodiversity. Additionally, the long-term nature of IPM strategies leads to more resilient and robust ecosystems.
IPM in Agricultural Practices:
In the realm of agriculture, IPM has gained widespread recognition for its ability to provide effective pest control without compromising soil health or the quality of crops. Farmers embracing IPM report improved yields, reduced production costs, and a decreased need for chemical inputs, showcasing the economic advantages of this approach.
Implementing IPM in Urban Settings:
IPM is not limited to agricultural settings; it’s equally applicable in urban environments. Whether managing pests in homes, parks, or public spaces, the principles of IPM can be adapted to create healthier living spaces without resorting to excessive pesticide use. This versatility makes IPM a valuable tool for sustainable pest management in diverse settings.
Championing Sustainable Practices:
As awareness grows regarding the environmental impact of traditional pest control methods, the adoption of IPM becomes a beacon of sustainability. By championing these integrated techniques, individuals, businesses, and communities contribute to a healthier planet while effectively managing pest issues.
Linking to Integrated Pest Management Techniques:
For those eager to embrace a holistic and sustainable approach to pest management, delve into the world of Integrated Pest Management Techniques at Integrated Pest Management Techniques. Explore how combining various strategies can create a harmonious environment, fostering coexistence with nature while effectively managing pest challenges.
Conclusion:
Integrated Pest Management stands as a testament to the power of a holistic and balanced approach in pest control. By integrating biological controls, cultural practices, and strategic pesticide use, IPM offers a sustainable solution that benefits ecosystems, agriculture, and urban settings alike. As we strive for a harmonious coexistence with nature, IPM emerges as a pivotal tool in creating a healthier and more resilient planet.
